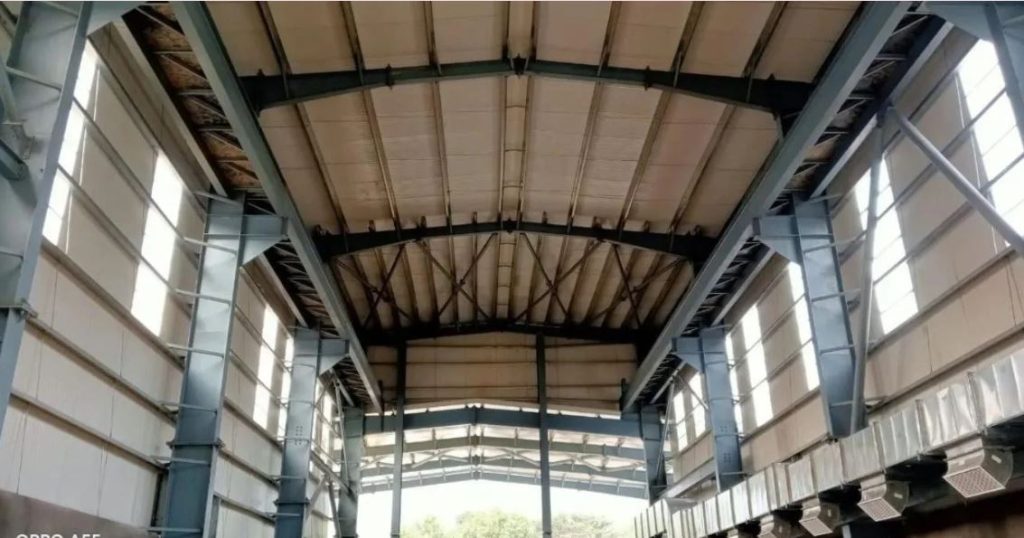
Pre-engineered structures, commonly referred to as PEBs, have transformed the landscape of modern construction. These structures have evolved significantly over the years, from their inception in the early 20th century to their current state of technological sophistication. Examining the past, present, and potential future developments in pre-engineered structures provides valuable insights into the ever-changing world of construction. This article discusses the various aspects of pre-engineered buildings, tracing their development from humble beginnings to their current state as innovative marvels of construction.
The Birth of Pre-Engineered Structures
In the early 20th century, the concept of pre-engineered structures emerged as a response to the need for rapid and cost-effective construction solutions. During this period, standardized components and materials became more readily available, allowing for the development of factory-fabricated structural elements. The first pre-engineered structures were primarily used for agricultural and industrial purposes due to their affordability and efficiency in accommodating large spaces.
The Present State of Pre-Engineered Structures
In the present day, pre-engineered structures have transcended their initial applications. These have become synonymous with versatility and efficiency, making them a popular choice for various sectors:
Commercial Spaces: Pre-engineered structures are increasingly used for commercial complexes, offices, and retail spaces. Their quick construction turnaround time and flexibility in design make them excellent for businesses looking to establish a presence swiftly.
Warehouses and Logistics: The logistics industry heavily relies on PEBs for their expansive storage facilities. The ability to customize these buildings to accommodate specific storage needs has contributed to their widespread use.
Sports and Recreational Facilities: Indoor sports arenas and recreational centers often employ pre-engineered building technology. The clear-span design of PEBs ensures that there are no obstructive columns, providing ample space for various activities.
Agricultural Buildings: Pre-engineered structures remain essential in agriculture, offering farmers cost-effective solutions for storage and processing facilities.
Educational Institutions: Schools and universities are adopting PEBs for their classroom buildings and gymnasiums due to their rapid construction and cost-efficiency.
Sustainability in Pre-Engineered Structures
The future of pre-engineered structures is intrinsically linked to sustainability. As environmental concerns grow, the construction industry is embracing eco-friendly practices. PEBs are no exception:
Energy Efficiency: The integration of energy-efficient insulation materials and systems has become a standard in PEBs, reducing their carbon footprint.
Solar Integration: Pre-engineered structures are increasingly designed to accommodate solar panels, harnessing renewable energy sources.
Recyclable Materials: The use of recyclable and sustainable materials in the construction of PEBs aligns with the global push for greener buildings.
Future Prospects
In addition to the advantages mentioned above, pre-engineered structures have several promising prospects:
Smart Building Integration: The incorporation of smart technologies for monitoring and controlling building functions will likely become more prevalent in PEBs.
Hybrid Structures: Combining the benefits of PEBs with traditional construction methods may result in hybrid structures that offer the best of both worlds.
Greater Customization: Advancements in design software will enable greater customization of pre-engineered structures, making them suitable for a wider range of architectural styles.
The evolution of pre-engineered buildings from their humble beginnings to their current prominence in the construction industry is a testament to human innovation and adaptability. With ongoing technological advancements and a growing emphasis on sustainability, these are positioned to play a pivotal role in the future of construction.